International Trade Terms and Export Payment Methods
Importance of International Trade: Global trade significantly contributes to the economic growth and prosperity of countries. It facilitates the exchange of goods and services between nations, creating market diversity and fostering a competitive environment. Importance of Trade Terms for Businesses: The correct use of trade terms ensures that international trade transactions are conducted efficiently and clearly. These terms clarify the distribution of responsibilities and costs between parties.
Fundamentals of International Trade
Understanding international trade is key to succeeding in the global economy. The history and fundamental principles of trade help in better grasping modern trade practices.
History of International Trade: Throughout history, trade routes like the Silk Road, Spice Route, and Amber Road have connected different civilizations and cultures. These routes have played a crucial role in the development of trade.
International Trade Terms and Definitions
International trade terms standardize and clarify trade transactions. These terms specify the responsibilities and cost distribution between parties.
What are Incoterms 2020?: Incoterms are rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers for the delivery of goods under sales contracts in international trade.
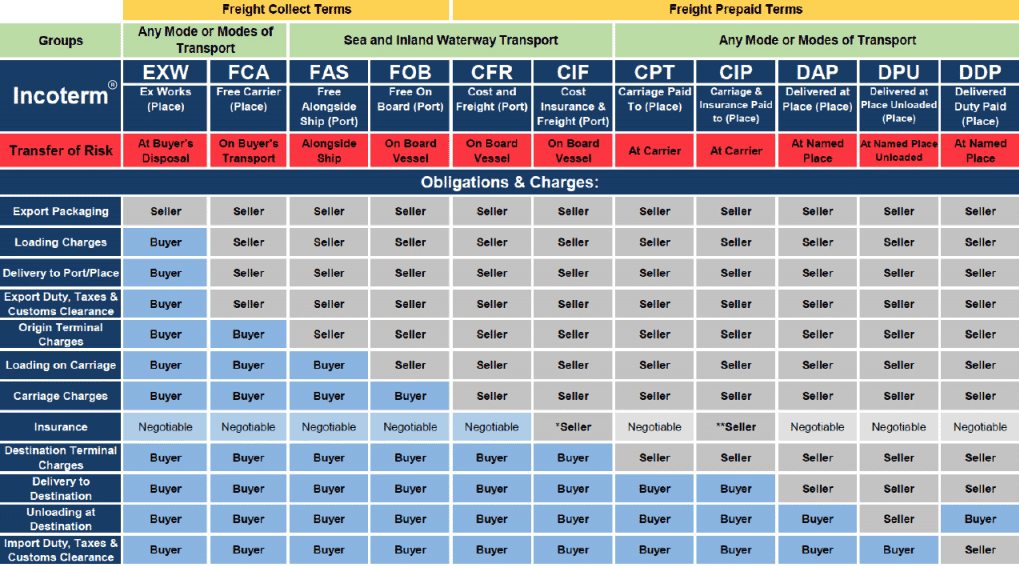
EXW (Ex Works): The seller makes the goods available at their premises or another named place (factory, warehouse, etc.). The seller does not bear the responsibility for loading the goods or clearing them for export.
FCA (Free Carrier): The seller delivers the goods to the carrier or another person nominated by the buyer at the seller's premises or another named place. The seller is responsible for export clearance.
CPT (Carriage Paid To): The seller pays for the carriage of the goods up to the named place of destination. However, the risk transfers to the buyer once the goods are handed over to the carrier.
CIP (Carriage and Insurance Paid To): The seller covers the transportation costs and minimum insurance up to the named place of destination. Risk transfers to the buyer once the goods are handed over to the carrier.
DAP (Delivered At Place): The seller bears all risks and costs of bringing the goods to the named place of destination. Delivery occurs when the goods are placed at the disposal of the buyer.
DPU (Delivered at Place Unloaded): The seller delivers and unloads the goods at the named place of destination. Risk and cost transfer to the buyer once the goods are unloaded.
DDP (Delivered Duty Paid): The seller assumes all costs, risks, and import customs formalities. Delivery occurs when the goods are placed at the disposal of the buyer.
FAS (Free Alongside Ship): The seller delivers the goods alongside the ship at the named port of shipment. Risk and cost transfer to the buyer at this point.
FOB (Free On Board): The seller loads the goods onto the ship at the named port of shipment. Risk and cost transfer to the buyer once the goods are on board.
CFR (Cost and Freight): The seller pays for the transportation to the named port of destination, but risk transfers to the buyer once the goods are on board the ship.
CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight): The seller covers the cost of transportation and minimum insurance up to the named port of destination. Risk transfers to the buyer once the goods are on board the ship.
Export and Import Terms
Export and import terms define the procedures and documents involved in the movement of goods across international borders. These terms ensure the correct and efficient management of customs processes.
Export Declaration: An export declaration is a document required for customs procedures when shipping goods abroad.
Import Declaration: An import declaration is a document required for customs clearance of goods brought into a country.
Trade Contracts
Trade contracts regulate the trade relationship between buyers and sellers. These contracts specify the rights and obligations of the parties and ensure the smooth progression of trade transactions.
Purchase-Sale Agreement: A purchase-sale agreement is a contract between a buyer and a seller that stipulates the terms of the sale.
Distribution Agreement: A distribution agreement is a contract for the distribution of a product within a specified region.

Export Payment Methods in Turkey
Cash Payment: The importer pays the exporter before the shipment of goods. This method is the least risky for exporters.
Letter of Credit: A payment method guaranteed by banks. The importer's bank guarantees payment to the exporter's bank upon fulfilling certain conditions. This method is secure for both parties.
Documents Against Payment: After the shipment of goods, the exporter sends the documents through their bank to the importer's bank. The importer pays the bank to receive the documents and, consequently, the goods.
Documents Against Acceptance: The importer commits to paying at a later date after receiving the goods. The exporter assumes more risk in this method.
Open Account: The exporter ships the goods and the importer pays at a later date. This method is usually preferred in trust-based relationships and is one of the riskiest for exporters.
Acceptance Credit: The importer commits to paying at a specified future date and provides a bill of exchange (check) to the exporter. The importer makes the payment on the specified date.
Bank Transfer: The importer pays the exporter before or after the shipment of goods via bank transfer. The terms can vary based on the agreement between the importer and exporter.
Logistics and Transportation Terms
Logistics and transportation terms ensure the efficient movement of goods along the supply chain. These terms explain the shipping process and related documents.
Freight: Freight is the charge for transporting goods.
Bill of Lading: A bill of lading is a document issued by the carrier acknowledging receipt of goods for shipment.
CMR Document: The CMR document is an international transport document used in road transport.
Storage and Inventory Management: Storage and inventory management involve the safe storage of goods and efficient management of inventory.
Customs and Taxation Terms
Customs and taxation terms regulate the legal and financial aspects of international trade. These terms ensure the compliant and efficient execution of import and export transactions.
Customs Declaration: A customs declaration is a document that must be submitted to customs for the import or export of goods.
Tariffs and Quotas: Tariffs and quotas are taxes and quantity limits applied to imported goods.
Bonded Warehouse: A bonded warehouse is a place where customs-controlled goods are stored temporarily.
Free Trade Agreements: Free trade agreements are treaties between countries aimed at reducing trade barriers.
Risk Management and Insurance Terms
Risk management and insurance terms ensure the security and sustainability of international trade. These terms provide protection against various trade risks.
Cargo Insurance: Cargo insurance covers the risk of damage or loss of goods during transportation.
Political Risk Insurance: Political risk insurance protects against risks arising from political events.
Commercial Risk Insurance: Commercial risk insurance covers financial risks arising from commercial transactions.
Trade Policies and Regulations
Trade policies and regulations define the international trade strategies of countries. These policies promote fair and free trade.
Trade Policy Instruments: Trade policy instruments are tools used by countries to define their trade policies.
Trade Blocs: Trade blocs are groups of countries that come together to increase economic integration.
World Trade Organization: The World Trade Organization regulates global trade rules.
European Union Trade Policy: The European Union Trade Policy includes the regulations and policies related to trade within the EU.
Future of International Trade
The future of international trade is shaped by new trends such as digitalization and sustainability. This section explores how trade will evolve in the future.
Digital Trade and E-Commerce: Digital trade and e-commerce cover trade conducted over the internet and the role of digital platforms.
Blockchain and Trade: Blockchain and trade involve the use of blockchain technology in trade and its advantages.
Sustainable Trade: Sustainable trade encompasses environmentally friendly and sustainable trade practices.


